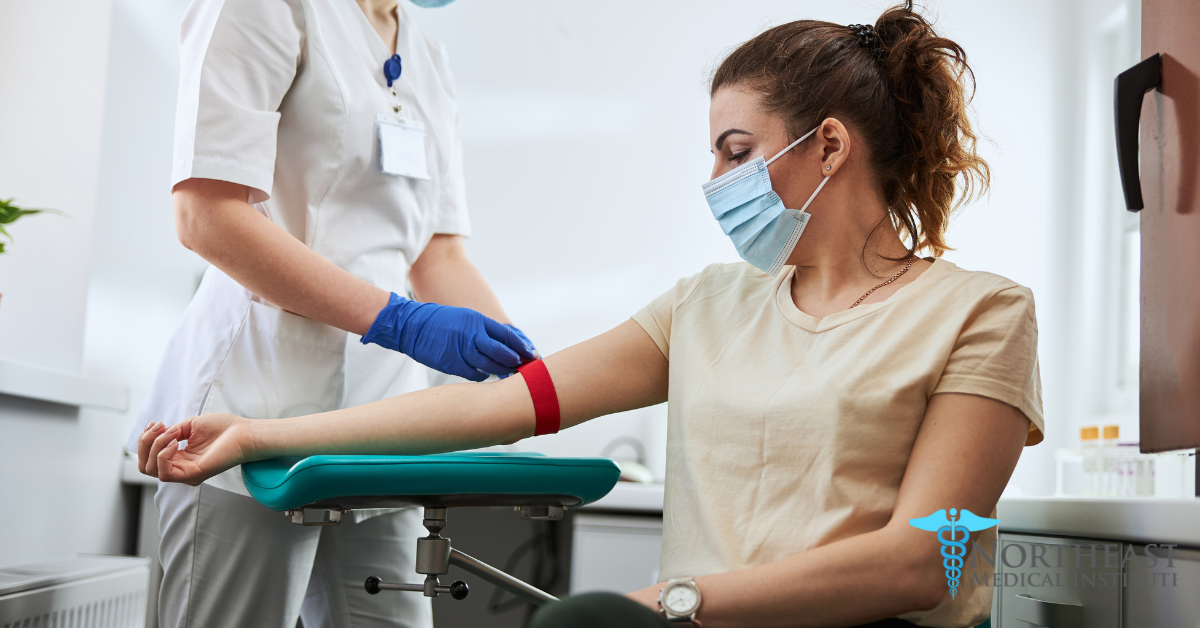
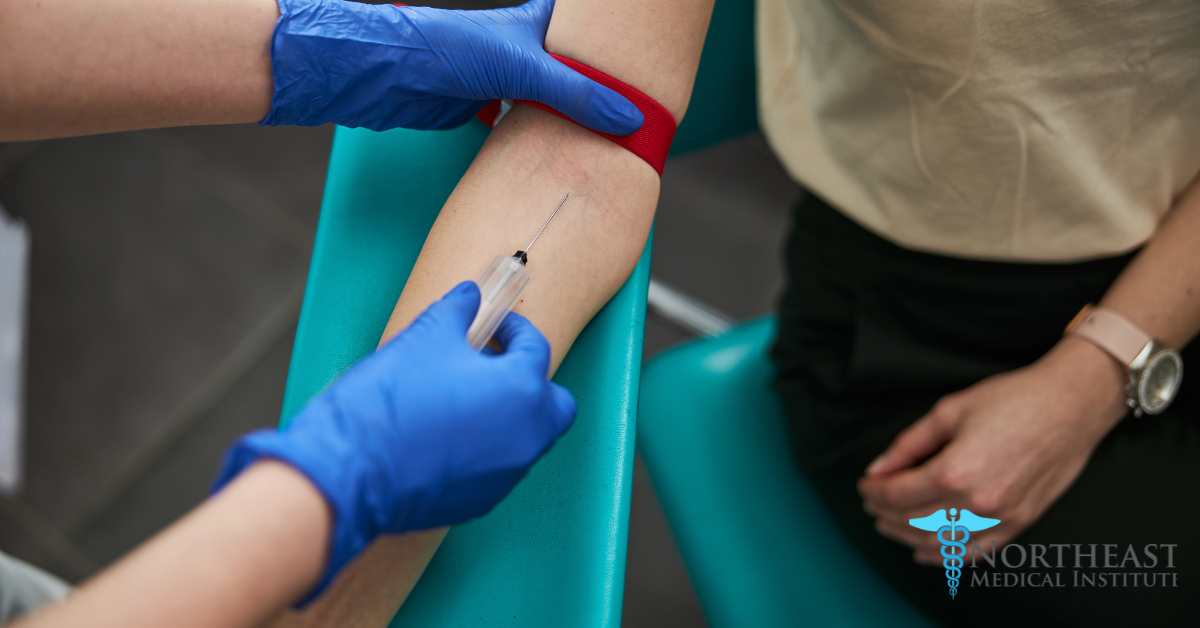
What does a phlebotomy technician do, and how can you become one? Phlebotomy technicians are healthcare professionals specializing in blood collection for testing and donations. In this article, you’ll learn about accredited training programs, the certification process, and uncover the career potential for those with the dedication to pursue this critical healthcare position.
Key Takeaways
- Phlebotomy technicians require a mix of technical and soft skills, including fine motor skills, emotional intelligence, knowledge of billing and coding, and the capacity to manage sterile environments; continuous education is integral to keeping up with technological advancements.
- State-approved phlebotomy technician programs are essential for aspirants, providing both theoretical knowledge and practical hands-on training; certification, though not mandatory in all states, is vital for phlebotomists and requires ongoing education for renewal every two years.
- The demand for phlebotomy technicians is growing with an expected 7.7% employment growth from 2022 to 2032, driven by an aging population and advancements in medical technology; certification opens a broad range of healthcare employment opportunities and potential career advancements.
Discover the Role of a Certified Phlebotomy Technician
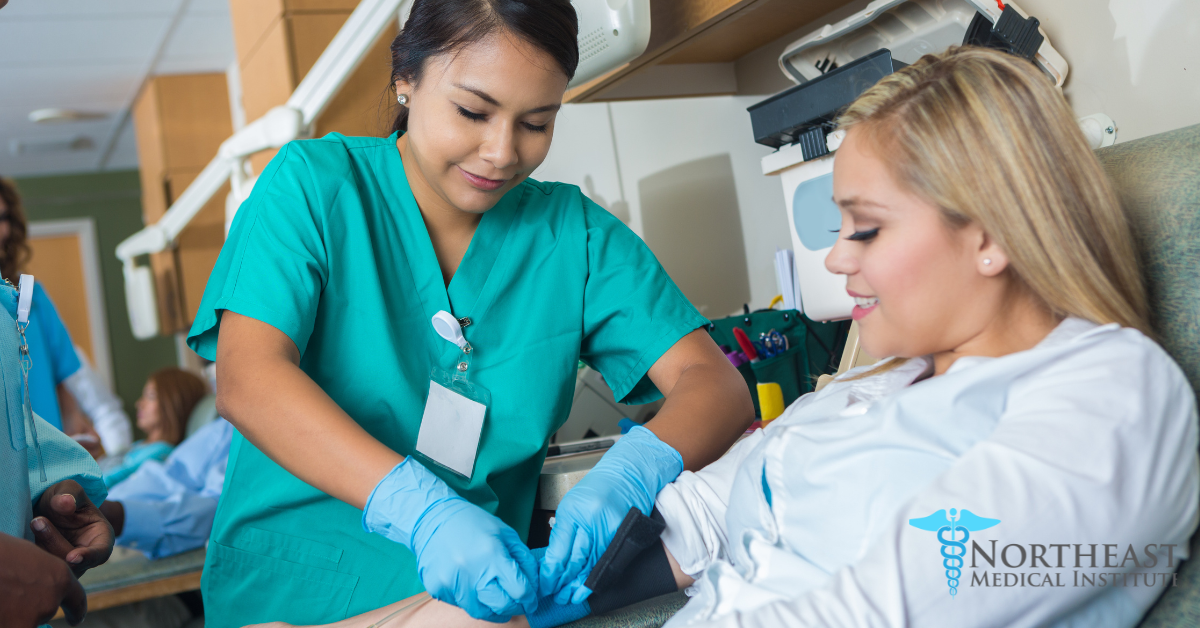
Phlebotomy technicians are healthcare professionals who are primarily responsible for collecting blood and preparing samples for testing. Beyond needlework, phlebotomy technicians play a crucial role in patient care. They are usually the first point of contact for patients, responsible for explaining procedures and ensuring the comfort of patients who may be apprehensive about needles.
What Does a Phlebotomist Do?
As phlebotomy technicians, their primary responsibility is to collect blood samples from patients, a process that involves confirming patient identities, locating suitable veins, and drawing blood using proper techniques. They employ various methods of blood collection, such as venipuncture, fingersticks, or heelsticks, depending on the patient’s condition and the required tests.
In addition to blood collection, phlebotomists may also perform basic point of care testing, which includes the analysis of blood samples at the time and place of patient care.
Essential Skills Every Phlebotomy Technician Should Have
Phlebotomy technicians require a variety of skills to excel in their profession. These include:
- Fine motor skills for accurate needle insertion
- Emotional intelligence for managing anxious patients
- Basic coding and billing knowledge
- The ability to work well with people under pressure
- Comfort with using computers and high-tech devices
- Understanding how medications and diet can influence blood samples
- Maintaining a sterile environment
These skills are essential for success in the field of phlebotomy.
As the healthcare industry evolves, proficiency in electronic health records systems and other relevant technologies is a must. To keep up with the evolving trends, continuous education programs are beneficial, helping phlebotomists to reflect on their identification procedures, minimizing risks of inaccuracies and enhancing the quality of patient care.
Phlebotomy Technician Program Essentials
For aspiring phlebotomists, the first step to launching their career is enrolling in a state-approved phlebotomy technician program. These programs offer comprehensive training on how to draw blood safely, manage procedural aspects, collect blood specimens, and perform venipuncture, in addition to covering theoretical knowledge on safety, infection control, legal issues in healthcare, and human anatomy and physiology. A typical phlebotomy training program comprises 40-80 classroom hours and 20-40 clinical hours of hands-on training.
Some programs, like the one at NVCC, go beyond the typical requirements by offering 200 hours of classroom instruction, simulated lab experience, and clinical validation opportunities at partner facilities. Before enrolling, it’s crucial to ensure that the phlebotomy training program is state-approved and to inquire about the location of clinical hours, whether it includes the certification exam, and the agency conducting the exam.
Curriculum Highlights
The curriculum of a Phlebotomy Technician program provides a solid foundation in medical knowledge and practical skills. It begins with foundational concepts in phlebotomy, advancing to complex phlebotomy equipment and procedures. Core subjects include medical terminology, anatomy and physiology, along with an introduction to healthcare legal issues and infection control. The hands-on training encompasses the practical skills needed to perform basic phlebotomy procedures, such as the proper collection of blood specimens and mastering venipuncture techniques.
The course is designed for:
- Those seeking employment as a Certified Phlebotomy Technician
- Certified Nurse Assistant professionals looking to advance in their career
- Individuals looking to change their career and enter the medical field
The instructors at Northeast Medical Institute embody excellence and represent the best in their field. The comprehensive phlebotomy program at Northeast Medical Institute offers education in necessary information and skill sets for professional phlebotomy.
Northeast Medical Institute offers flexible scheduling options to accommodate students’ needs and provides assistance for transitioning to a healthcare career after completing the phlebotomy program.
Clinical Practicum Experience
The clinical practicum is an essential component of a phlebotomy training program, allowing students to gain hands-on experience in a real-world setting. These lab/clinical hours prepare students for actual situations they will encounter in their work. A Certificate of Competency in Phlebotomy Practicum requires a total of 120 clock hours, providing structured experience in clinical settings. Under the guidance of experienced instructors, students enhance their skills with hands-on experience in in-person phlebotomy lab sessions.
The clinical practicum experience includes 20-40 hours of clinical experience where students can apply learned skills in healthcare environments such as hospitals, medical labs, and blood drives.
Navigating Certification Requirements
Once you’ve completed your phlebotomy technician training, the next step is to get certified. Certification for phlebotomy technicians varies by organization, usually requiring completion of a training program and sometimes work experience. Although not legally required in most states, certification from a recognized body signifies mastery of essential skills and is preferred or required by many employers for phlebotomy positions.
The primary phlebotomy certifications that are nationally recognized include Phlebotomy Technician (PBT), Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT), and Registered Phlebotomy Technician (RPT). It’s worth noting that California, Washington, Louisiana, and Nevada require phlebotomists to be certified or licensed, making these states exceptions to the typical non-mandated certification landscape. Certified Phlebotomy Technicians must renew their certification every two years to keep their credential current. This ensures that they stay up-to-date with the latest industry standards and best practices.
Preparing for the Certification Exam
The phlebotomy certification exam is designed to assess candidates on the following:
- Workplace safety
- Infection control
- Patient safety
- Phlebotomy techniques
The exam features scenario-based questions that test candidates’ abilities to respond to hypothetical situations in a medical setting.
A Certificate of Completion from a phlebotomy training class is required to sit for the national certification exam; however, it does not itself confer a certified status. The National Healthcareer Association’s Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT) exam is recommended for individuals who complete the Phlebotomy training program.
The National Phlebotomy Solutions (NPS) certification includes the following:
- Study materials
- Practice exams
- One attempt at the final certification exam
- Professional resume revision
The certification, which can be completed online, has a fee of $200.
After Successful Completion: Next Steps
Once you’ve successfully completed your phlebotomy training and certification, the world of healthcare is your oyster. As a certified phlebotomist, you can explore several career paths such as:
- Medical assistant
- EKG technician
- Clinical lab technician
- Registered nurse
- Physician’s assistant
For those interested in advancing their careers, additional certifications and education may be required, especially when facing difficulty finding employment in their desired field.
For instance, the role of a physician’s assistant, which requires a master’s degree, is another advanced career option for phlebotomists with an understanding of medical terminology and patient interaction.
Educational Pathways: Enroll in a Phlebotomy Technician Training Program
To embark on a career in phlebotomy, the first step is gaining the required educational qualifications. The most fundamental requirement is completing a high school degree or an equivalent credential. Before enrolling in a phlebotomy training program, candidates in New Haven must also provide proof of a clean background check, negative hepatitis and TB tests, as well as updated immunization records.
Phlebotomy training courses are typically designed to be completed in one to two semesters, equivalent to 4 to 8 months, which is necessary before pursuing professional certification. While a GED or high school diploma may not be mandatory for enrolling in the Phlebotomy Technician Program, it is required to qualify for the NHA CPT Testing.
Enrollment Process Simplified
Enrolling in a Phlebotomy Technician Program is a straightforward process that includes comprehensive coursework, such as phlebotomy skills, specimen processing, and preparation for certification exams. Many programs offer hybrid options that allow students to combine at-home study with in-person lab sessions, offering a mix of convenience and essential practical experience.
For those with unique schedule needs, programs such as the two-week accelerated Phlebotomy Technician Program at Northeast Medical Institute may be suitable. Students can register for phlebotomy technician programs on an ongoing basis, ensuring opportunities to enroll for upcoming classes are consistently available.
Understanding the Cost and Financial Assistance Options
While pursuing a career in phlebotomy can be a fulfilling choice, it’s also important to understand the financial aspects of your education. Financial assistance for the Phlebotomy Technician Program at Northeast Medical Institute includes the possibility of qualifying for the WIOA program and access to a 6-month financing plan to help manage the cost of the training program.
Career Outlook for Phlebotomy Technicians
The career outlook for phlebotomy technicians is promising. The demand for these professionals is increasing significantly, driven by an essential need for blood testing in healthcare and growth due to medical advancements and an aging population. The projected employment growth rate for phlebotomy technicians is set at 7.7% from 2022 to 2032. An estimated 10,800 job openings for phlebotomists are expected to become available over the decade from 2022 to 2032.
In 2022, the median salary for phlebotomists was $38,530, with the potential to earn up to $45,280 or as low as $35,020 depending on individual performance and experience.
Finding Employment Opportunities
With a certification in hand, phlebotomy technicians can find a wealth of employment opportunities in various healthcare settings. These settings include:
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic laboratories
- Blood donor centers
- Clinics
- Other medical facilities
Phlebotomists may have varied work schedules, including day, evening, or night shifts, depending on the healthcare setting.
The Future of Phlebotomy in Healthcare
The future of phlebotomy in healthcare is exciting. Some of the trends shaping the field include:
- Technological advancements in blood collection devices
- The integration of electronic health records
- The emergence of personalized medicine and genetic testing
These advancements are expected to have a significant impact on the field of phlebotomy.
There is also a growing demand for mobile phlebotomy services as home healthcare becomes more prevalent, requiring phlebotomists to adapt to working in non-traditional settings. The rise in personalized medicine and genetic testing is leading to a need for phlebotomists to collect specialized blood samples and be knowledgeable about these areas.
Real-World Applications: Phlebotomy Skills in Action
The skills acquired through a phlebotomy training program have essential real-world applications. This training begins with practicing on a simulated arm, which allows budding phlebotomists to become familiar with the technique in a controlled environment.
The educational process progresses from a fake arm to real-life scenarios where they apply their skills to draw blood from patients.
From Classroom Instruction to Patient Care
The journey from the classroom to patient care is transformational. Theoretical knowledge and practical skills acquired in the classroom, which the curriculum covers, translate into an improved approach towards patient identification and sample handling by technicians.
Competency in the Lab and Beyond
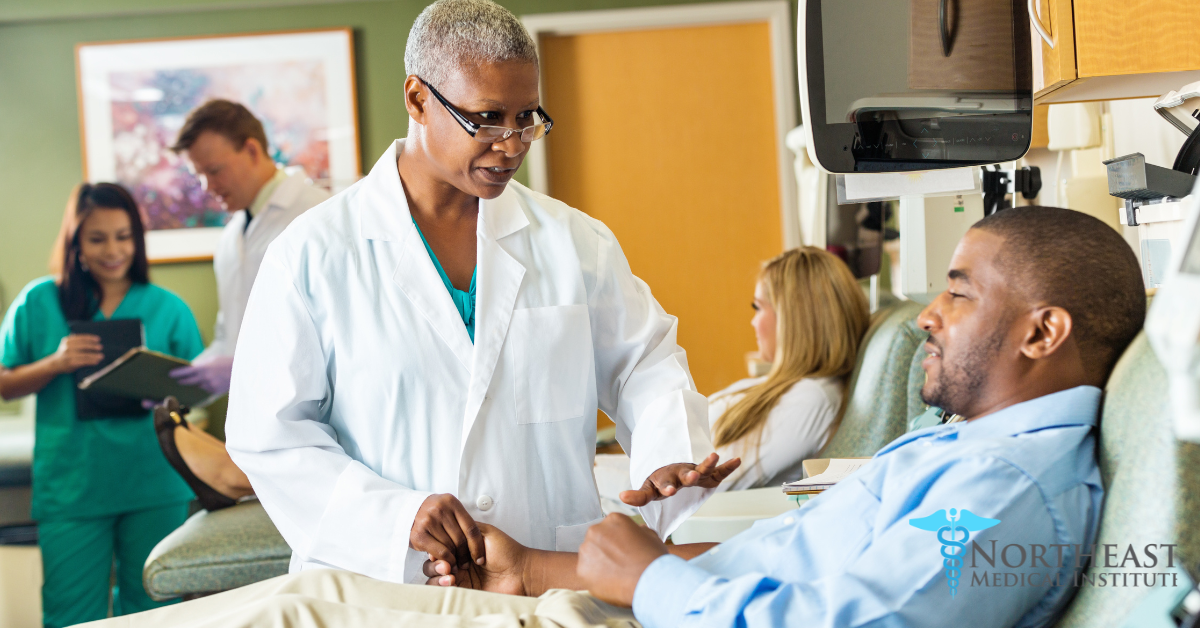
Competency in the lab is just as important as it is in the field. Phlebotomy technicians not only draw blood but also play a crucial role in taking vital signs, such as blood pressure, pulse, and respiration. Mastery of various competencies, including fine motor skills for needle insertion, patient emotion management, and adherence to safety protocols, is essential for success.
Advancement Opportunities for Phlebotomy Technicians
Phlebotomy is an entry-level role in laboratory sciences, providing a foundation for further education and career advancement within healthcare. Phlebotomy technicians can advance their careers by assuming management or supervisory roles in healthcare settings.
Another avenue for advancement is specializing as a donor phlebotomy technician, which allows technicians to focus their skills and enhance their qualifications.
Specializations Within Phlebotomy
The field of phlebotomy offers several specializations that can enhance a technician’s career. Phlebotomists can enhance their career by specializing through certifications such as collections phlebotomy specialist, registered phlebotomy specialist, or patient service technician specialist. These specializations typically require prior experience in the field and are often provided by the employers of phlebotomy technicians themselves.
For those interested in further advancement, phlebotomists have the opportunity to become medical laboratory technicians (MLT) by pursuing further education with an associate’s degree and completing an accredited MLT training program. With additional experience and education, medical laboratory technicians can advance their careers to become medical technologists (MT).
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education and professional development are crucial for staying at the forefront of the phlebotomy field. Phlebotomists can participate in continuing education courses offered by organizations like AMT, which provide webinars, articles, and online courses to stay current on phlebotomy practices. These courses cover a range of topics, from the total testing process to needlestick injury prevention and improving venipuncture training methods.
It’s also possible for phlebotomists to become Certified Phlebotomy Instructors (CPI) entirely through online training programs, provided they have over 5 years of experience in the field.
Summary
Phlebotomy technicians play a critical role in healthcare, making the field an exciting and fulfilling career choice. From understanding the role of a phlebotomy technician to navigating the certification requirements, the journey to becoming a phlebotomist requires dedication, skill, and continuous learning. With various career advancement opportunities and a promising career outlook, the world of phlebotomy offers endless possibilities to those who are just as passionate about learning as they are about patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary duties of a phlebotomy technician?
The primary duties of a phlebotomy technician include collecting blood samples from patients by confirming identities, locating veins, and drawing blood using proper techniques, as well as performing basic point of care testing.
What are some specializations within phlebotomy?
Phlebotomists can specialize through certifications such as collections phlebotomy specialist, registered phlebotomy specialist, or patient service technician specialist. These specializations allow phlebotomists to develop expertise in specific areas of the field.
What are the requirements for becoming a Certified Phlebotomy Instructor (CPI)?
To become a Certified Phlebotomy Instructor (CPI), a phlebotomist needs over 5 years of experience in the field.
What are the career advancement opportunities for phlebotomy technicians?
Phlebotomy technicians can advance their careers by taking on management or supervisory roles in healthcare settings or specializing as a donor phlebotomy technician. Consider exploring these opportunities to progress in your career.
What does the phlebotomy certification exam assess?
The phlebotomy certification exam assesses candidates on workplace safety, infection control, patient safety, and phlebotomy techniques, ensuring they have the necessary skills and knowledge for safe and effective practice.