Certificate of Phlebotomy: Your Complete Guide to Getting Started in Healthcare
The healthcare industry continues to expand rapidly, creating thousands of new opportunities for skilled professionals. A phlebotomist is a healthcare professional who specializes in drawing blood samples for medical testing and diagnosis. Among these growing career paths, phlebotomy stands out as an accessible entry point that requires minimal training time while offering stable employment prospects, especially in lab settings where certified professionals are in high demand. A certificate of phlebotomy serves as your gateway to this rewarding field, providing the credentials and knowledge needed to begin drawing blood and collecting specimens in various healthcare settings. The employment of phlebotomists is projected to increase faster than the average for all occupations, reflecting the growing demand for diagnostic and laboratory services.
Whether you’re a recent high school graduate exploring healthcare careers or a professional seeking a career change, understanding the ins and outs of phlebotomy certification can help you make an informed decision about your future. Enrolling in a phlebotomy course is the first step toward becoming a certified phlebotomist and starting a career in laboratory sciences. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about earning your phlebotomy technician certificate, from program options to career opportunities. Phlebotomy Technician programs vary in length and can include both online and hybrid formats, offering flexibility to suit different learning preferences and schedules.

What is a Certificate of Phlebotomy
A certificate of phlebotomy is an official credential that certifies completion of phlebotomy training and demonstrates competency in blood collection procedures. This certification verifies that you have successfully completed the necessary education and training to work as a phlebotomy technician in hospitals, clinical laboratories, and other healthcare facilities.
Most phlebotomy programs require approximately 170 hours of coursework combined with 100 clinical hours where students perform supervised venipunctures on actual patients. During this training, students master essential skills including drawing blood, specimen processing, patient communication, and safety protocols required in the clinical laboratory sciences field. Qualified faculty play a crucial role in delivering instruction, guiding students through the phlebotomy course, and supervising clinical practice to ensure competency. Each draw must be supervised and signed off on a blood draw log and externship forms provided to students. Students are required to complete a clinical component involving 30 supervised venipunctures as a core requirement to graduate from their Phlebotomy Technician program.
Upon graduation from an accredited phlebotomy program, graduates are eligible to work as certified phlebotomy technicians across various healthcare settings. The certificate demonstrates to employers that you possess the skills needed to safely collect blood specimens, handle laboratory testing requirements, and interact professionally with patients in both routine and challenging situations. Students who complete the full Phlebotomy Technician Certification Program will earn Continuing Education Units (CEUs) from recognized professional organizations, supporting their ongoing professional development and certification maintenance.
The immediate career benefits of earning a phlebotomy technician certificate include:
- Access to entry-level positions in hospitals, diagnostic labs, and outpatient clinics
- Competitive starting salaries with opportunities for advancement
- Stable employment in a growing healthcare sector
- Foundation for pursuing advanced allied health careers
- Flexibility to work in various healthcare environments
Phlebotomists typically enjoy competitive pay, benefits, and job satisfaction.
Types of Phlebotomy Certificate Programs
Modern phlebotomy education offers multiple program formats to accommodate different learning preferences and schedules. Understanding these options helps prospective students choose the approach that best fits their lifestyle and career timeline. Students may complete the Online Phlebotomy Technician course in as little as 4 weeks, making it an attractive option for those seeking a quick entry into the field.
Online Phlebotomy Certificate Programs
Online programs provide maximum flexibility with self-paced learning and 24/7 access to course materials. These programs typically cover the theoretical components of phlebotomy through interactive modules, video demonstrations, and virtual simulations. Students will collaborate with their instructors by submitting videos demonstrating phlebotomy techniques and receiving personalized feedback to improve their skills. Students can complete coursework around work and family commitments, making this option ideal for busy adults seeking career transitions.
However, online programs still require hands-on clinical experience, which must be arranged separately through approved clinical sites or externship programs. Some online providers offer assistance with clinical placement, while others require students to secure their own training locations. Students are responsible for securing their own internship, but instructors can provide letters to assist with securing one.
On-Campus Certificate Programs
Traditional on-campus programs range from intensive 6-credit hour formats to comprehensive 9-week courses. These programs provide immediate access to instructors, laboratory equipment, and hands-on training opportunities. The structured classroom environment allows for real-time feedback and collaborative learning with fellow students.
Campus-based programs often include integrated clinical rotations, eliminating the need for students to independently arrange practical experience. This format works well for students who prefer face-to-face instruction and benefit from the accountability of scheduled class attendance.
Online Phlebotomy Certificate Programs
Online programs provide maximum flexibility with self-paced learning and 24/7 access to course materials. These programs typically cover the theoretical components of phlebotomy through interactive modules, video demonstrations, and virtual simulations. Students can complete coursework around work and family commitments, making this option ideal for busy adults seeking career transitions. Students can take the NAPTP National Phlebotomy Certification Exam online after course completion.
Hybrid programs combine online coursework with hands-on clinical training, offering a balanced approach that maximizes both flexibility and practical experience. Students complete theoretical components online while attending scheduled laboratory sessions and clinical rotations at designated facilities. A virtual alternative is available for all Phlebotomy Technicians who enroll in a Phlebotomy Technician program, ensuring accessibility for students in remote locations or with limited clinical site access.
Hybrid programs combine online coursework with hands-on clinical training, offering a balanced approach that maximizes both flexibility and practical experience. Students complete theoretical components online while attending scheduled laboratory sessions and clinical rotations at designated facilities.
This format appeals to students who want some schedule flexibility but recognize the value of in-person instruction for technical skills development. Hybrid programs often feature accelerated timelines while maintaining comprehensive curriculum coverage.
Tuition-Free Programs
Some prestigious institutions like Mayo Clinic offer tuition-free phlebotomy technician training programs supported by workforce development scholarships. These competitive programs typically require applications and may have limited enrollment, but they provide exceptional training without the financial burden.
Tuition-free programs often partner with major healthcare employers, creating direct pathways to employment upon completion. While these opportunities are limited, they represent excellent value for students who meet eligibility requirements and can commit to the specified schedule.
Northeast Medical Institute Phlebotomy Program
Northeast Medical Institute offers a comprehensive phlebotomy technician certificate program designed to prepare students for immediate employment in healthcare settings. Their program combines classroom instruction with hands-on clinical experience, emphasizing proper blood collection techniques, specimen processing, and patient care. The curriculum aligns with national certification exam requirements and includes supervised clinical rotations at affiliated healthcare facilities.
Students at Northeast Medical Institute benefit from small class sizes, experienced instructors, and personalized support throughout the program. The institute assists with clinical site placement and provides guidance on the certification exam application process. Graduates of the Northeast Medical Institute phlebotomy program are well-prepared to enter the workforce as competent phlebotomy technicians, equipped with the skills needed for success in hospitals, laboratories, and outpatient clinics.
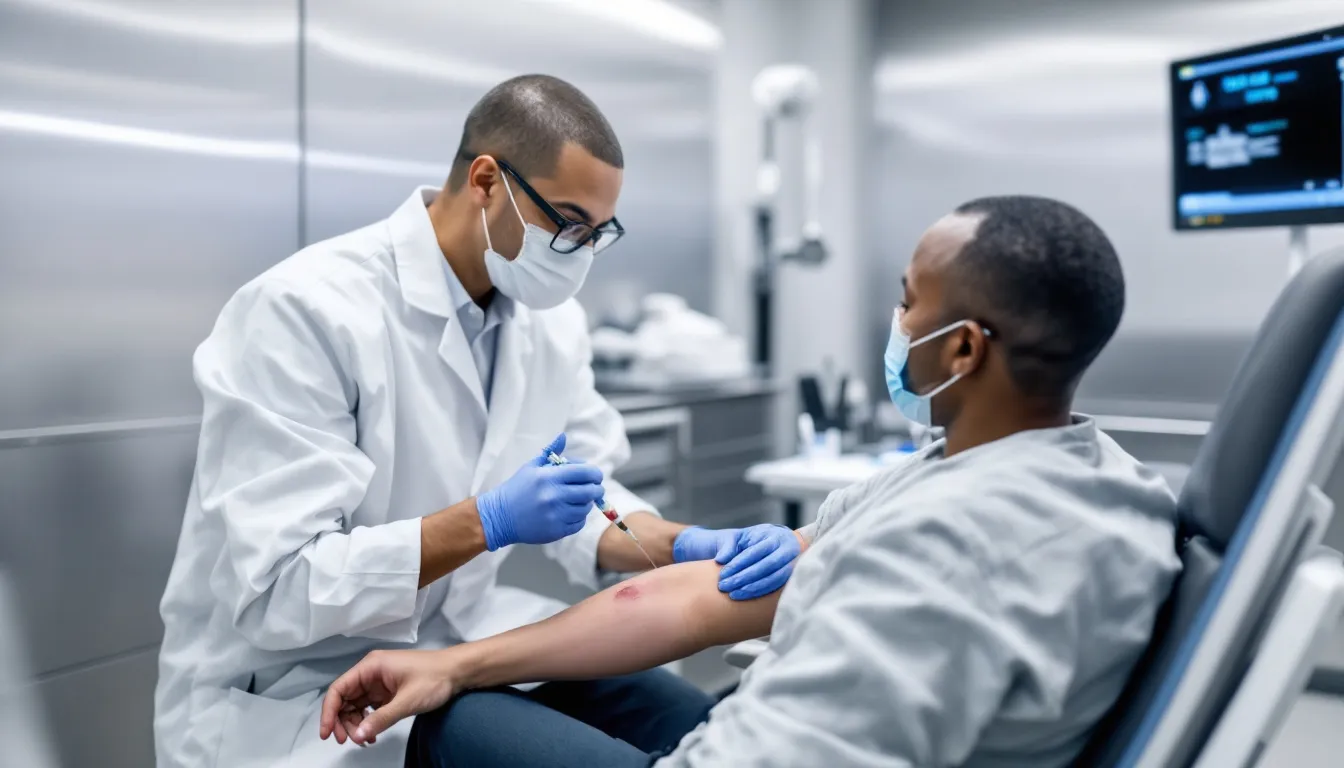
Certificate Requirements and Prerequisites
Before enrolling in any phlebotomy technician program, applicants must meet specific admission requirements and complete necessary clearances. Understanding these prerequisites helps prospective students prepare for the application process and avoid delays in starting their education. Some states, like California, require all phlebotomists to be certified before they can practice, making it essential to choose a program that meets state-specific requirements.
Educational Requirements
A high school diploma or GED serves as the foundational requirement for enrollment in most phlebotomy programs. Applicants are typically required to submit proof of high school diploma or equivalent as part of the admission process. Unlike many healthcare careers that require extensive prerequisite coursework, phlebotomy training welcomes students with basic secondary education completion. This accessibility makes phlebotomy an attractive option for individuals seeking quick entry into healthcare careers.
No prior medical experience is required to start phlebotomy certificate training, though any healthcare background can be beneficial. Students from diverse educational and professional backgrounds successfully complete phlebotomy programs and find employment in the field.
Background and Health Clearances
Healthcare facilities maintain strict safety standards, requiring all personnel to complete comprehensive clearance processes. Phlebotomy students must obtain:
- Criminal background check from local and federal databases
- Child abuse clearance in states where applicable
- Negative drug screening results
- Proof of immunity to communicable diseases
- Current vaccination records including hepatitis B, MMR, and seasonal flu
- Tuberculosis test results (usually chest X-ray or skin test)
All documentation must be uploaded by the applicant and verified by the program or service provider.
The clearance process can take several weeks to complete, so prospective students should begin gathering documentation early in their application timeline. Some programs offer conditional acceptance pending clearance completion, while others require all documentation before enrollment.
Physical and Technical Requirements
Phlebotomy work requires specific physical capabilities and technical skills. Students should be able to:
- Stand for extended periods during clinical rotations
- Manipulate small medical equipment and needles with precision
- Communicate effectively with patients and healthcare team members
- Handle potentially stressful situations involving blood and medical procedures
- Meet visual and manual dexterity requirements for safe venipuncture
Program directors typically provide detailed information about physical requirements during the application process, allowing students to assess their suitability for the profession before enrollment.
Curriculum and Training Components
Accredited phlebotomy programs provide comprehensive education covering 35 individual course topics essential for safe and effective blood collection. The curriculum balances technical procedures with patient care skills, preparing graduates for diverse healthcare environments.
Core Technical Training
Venipuncture techniques form the foundation of phlebotomy education, with extensive training on proper needle insertion, blood draw procedures, and specimen collection protocols. Students learn to work with various types of equipment, from traditional syringes to modern vacuum tube systems, ensuring adaptability across different healthcare settings. Certification requires completing a training program covering topics like anatomy, infection control, and proper venipuncture techniques. Courses in Phlebotomy Technician programs often cover proper phlebotomy technique, specimen processing, patient care, and anatomy and physiology, providing a well-rounded education.
Specimen processing training covers proper handling, labeling, and transportation of blood specimens to maintain sample integrity throughout laboratory testing procedures. This knowledge proves critical for accurate diagnostic results and patient safety.
Anatomy and Physiology Focus
Understanding circulatory system anatomy enables phlebotomists to locate suitable veins, recognize potential complications, and adapt techniques for different patient populations. Coursework covers vein location, blood flow patterns, and physiological factors affecting successful blood draws.
Students also learn about various blood components, their functions, and how different collection methods impact laboratory testing results. This knowledge supports effective communication with laboratory personnel and ensures appropriate specimen handling.
Communication and Patient Care
Laboratory communication skills prepare graduates to interact professionally with patients, families, and healthcare team members. Training includes techniques for explaining procedures, addressing patient concerns, and maintaining confidentiality in accordance with HIPAA regulations.
Patient care training emphasizes cultural sensitivity, age-appropriate communication strategies, and techniques for working with anxious or difficult patients. These skills prove essential for building trust and ensuring positive patient experiences during blood collection procedures.
Safety and Ethical Training
CPR and First Aid training prepares students to respond to medical emergencies that may occur during blood collection procedures. This certification often serves as a prerequisite for employment in many healthcare facilities.
Equipment usage training covers proper handling, maintenance, and disposal of medical supplies and devices. Students learn infection control protocols, personal protective equipment use, and waste management procedures required in healthcare environments.
Documentation and ethical considerations training ensures graduates understand legal requirements, patient rights, and professional responsibilities. This knowledge supports compliance with healthcare regulations and protects both patients and healthcare facilities.
Specialized Procedures
Non-blood specimen collection procedures expand graduate capabilities to include urine, stool, and other sample types commonly required for laboratory testing. This versatility increases employment opportunities and provides comprehensive diagnostic support skills.
Basic laboratory skills training may include specimen preparation, simple testing procedures, and quality control measures depending on program focus and available equipment.
Clinical Experience and Externships
Hands-on clinical experience represents the most critical component of phlebotomy education, transforming theoretical knowledge into practical skills through supervised patient interactions. This experience ensures graduates can confidently perform procedures in real healthcare environments.
Clinical Hour Requirements
Most certification programs require a minimum of 100 clinical hours combined with 100 supervised venipunctures to meet certification requirements. These hours must be completed at approved clinical sites under the supervision of qualified healthcare professionals.
Additionally, students typically must complete 30 documented blood draws in urgent care centers, hospitals, or clinics to demonstrate competency across diverse patient populations. This requirement ensures graduates can adapt their skills to different healthcare settings and patient needs.
Clinical Site Placement
Traditional programs arrange clinical rotations at partner healthcare facilities, providing students with guaranteed placement opportunities. These partnerships often lead to employment opportunities, as clinical sites frequently hire successful extern students.
Students gain advanced clinical experience in a hospital setting, which provides exposure to inpatient care and complex procedures. Students also gain practical experience in outpatient laboratories, blood donor centers, and physician offices. This exposure helps students identify their preferred work environment while building professional networks within the healthcare community. Some programs, like those at Mayo Clinic, provide a large number of clinical rotations for practical experience, ensuring students are well-prepared for real-world challenges.
Alternative Training Options
For students unable to secure in-person externships due to geographic or scheduling constraints, some programs offer Virtual Simulation Kit (VSK) options. These technology-based alternatives provide realistic training scenarios while accommodating students in remote locations or with limited clinical site access.
VSK training typically includes advanced simulation software, practice materials, and remote supervision to ensure students develop necessary skills. While not identical to traditional clinical experience, these programs meet certification requirements and prepare graduates for successful employment.
Mentorship and Professional Development
Clinical rotations provide mentorship from full-time professionals who guide students through real-world challenges and share practical insights about career development. These relationships often extend beyond training, providing ongoing support as new graduates establish their careers.
Many programs facilitate letters of recommendation from clinical supervisors, enhancing graduate competitiveness in the job market. Strong clinical performance can also lead to direct employment offers from externship sites.
Certification Exams and Accreditation
Upon completing phlebotomy technician training, graduates must pass national certification exams to work as certified phlebotomists. Understanding the various certification options and accreditation requirements helps students choose programs that align with their career goals. Certification signals a dedication to the profession, instilling trust in patients and employers while enhancing career prospects. The Phlebotomy Technician Certification from various programs is typically valid in the United States and Canada.
Primary Certification Examinations
The ASCP-PBT (Phlebotomy Technician Board of Certification) exam represents the gold standard in phlebotomy certification, with many programs achieving 100% pass rate goals. This comprehensive exam tests technical knowledge, safety protocols, and professional practices essential for competent phlebotomy practice.
The NAPTP National Phlebotomy Certification Exam and the NHA Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT) Exam provide widely recognized credentials offered by accredited programs. The NAPTP exam focuses on practical skills and theoretical knowledge required for entry-level phlebotomy positions across various healthcare settings.
Both exams require thorough preparation through coursework and practical experience, with most programs providing specific exam preparation resources and practice testing opportunities.
Additional Certification Options
Several other organizations offer phlebotomy certification exams, providing alternatives for graduates with different educational backgrounds or career focuses:
- NCCT (National Center for Competency Testing) certification
- AMT (American Medical Technologists) certification
- AMCA (American Medical Certification Association) certification
- NHA (National Healthcareer Association) certification
Other national exams from organizations like AMT, NHA, AMCA, and NCCT may require in-person testing. Each certification exam has specific eligibility requirements, testing formats, and renewal procedures. Students should research employer preferences in their geographic area to determine which certifications provide the best employment opportunities.
- NCCT (National Center for Competency Testing) certification
- AMT (American Medical Technologists) certification
- AMCA (American Medical Certification Association) certification
- NHA (National Healthcareer Association) certification
Each certification exam has specific eligibility requirements, testing formats, and renewal procedures. Students should research employer preferences in their geographic area to determine which certifications provide the best employment opportunities.
Program Accreditation Standards
NAACLS (National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences) accreditation ensures programs meet rigorous educational standards and provide quality training that prepares graduates for successful careers. Accredited programs undergo regular review and must demonstrate student success rates, employment outcomes, and curriculum quality.
Attending NAACLS accredited programs often serves as a prerequisite for taking certain certification exams and may be required by employers or state licensing boards. Prospective students should verify accreditation status before enrollment to ensure their education meets industry standards. Students are encouraged to review the program handbook or website for additional information on mission, accreditation, outcomes, policies, clinical sites, and contact details.
Certification Maintenance
Most certifications require ongoing continuing education to maintain active status. Requirements typically include:
- Annual renewal fees
- Continuing education credit hours
- Documentation of professional development activities
- Periodic re-examination or competency assessment
Understanding maintenance requirements helps graduates plan for long-term career development and ensures continued eligibility for employment in regulated healthcare environments.
Career Opportunities with a Phlebotomy Certificate
Earning a phlebotomy technician certificate opens doors to diverse employment opportunities across the healthcare industry. The growing demand for diagnostic laboratory testing creates strong job prospects for qualified phlebotomy technicians. Certified phlebotomists generally earn higher salaries than their non-certified counterparts, making certification a valuable investment in career advancement.
Employment Settings
Hospitals represent the largest employment sector for phlebotomists, offering opportunities in emergency departments, intensive care units, general medical floors, and outpatient laboratories. Hospital positions often provide comprehensive benefits, advancement opportunities, and exposure to diverse patient populations.
Diagnostic laboratories employ phlebotomists for routine blood collection, specialized testing procedures, and specimen processing activities. These positions typically offer regular schedules and focus on high-volume sample collection and processing.
Blood donor centers and plasma collection facilities provide specialized opportunities focusing on healthy donor populations. These positions often emphasize customer service skills alongside technical competencies.
Physician offices and outpatient clinics offer phlebotomy positions with more predictable schedules and ongoing patient relationships. These settings appeal to professionals who prefer consistent work environments and regular patient interactions.
Employment Success Rates
Current data indicates that 95% of graduates find employment in phlebotomy-related fields after certification, demonstrating strong demand for qualified professionals. This high placement rate reflects the essential nature of blood collection services across all healthcare sectors.
Many graduates secure employment at their clinical rotation sites, highlighting the value of strong performance during training. Building professional relationships during externships often leads to immediate job offers upon graduation.
Salary Expectations
Starting salaries for certified phlebotomists range from $26,301 to $32,448 annually, depending on geographic location, facility type, and experience level. Metropolitan areas and specialized healthcare facilities typically offer higher compensation packages.
Experience and additional certifications can lead to salary increases and advancement opportunities. Some phlebotomists pursue supervisory roles, specialized procedures, or transition into related healthcare careers with higher earning potential.
Career Advancement Pathways
Phlebotomy certification provides a strong entry point into healthcare with multiple advancement opportunities. Many phlebotomists use their experience as a foundation for pursuing nursing programs, medical assistant training, or advanced laboratory technician roles.
The practical healthcare experience gained through phlebotomy work provides valuable background for medical school applications, physician assistant programs, or other advanced healthcare degrees. This experience demonstrates commitment to healthcare careers and provides clinical exposure that strengthens applications for competitive programs.
Some phlebotomists advance to supervisory positions, training coordinators, or specialized roles in research laboratories or blood banking facilities. These positions typically require additional education or certification but build upon the foundation provided by initial phlebotomy training.

Program Costs and Duration
Understanding the financial investment and time commitment required for phlebotomy certification helps prospective students make informed decisions about their education. Program costs and duration vary significantly depending on format, location, and institutional type.
Typical Program Costs
Certificate programs typically range from $1,220 total cost including tuition, fees, and supplies for basic programs to several thousand dollars for comprehensive offerings. This cost structure makes phlebotomy training accessible compared to other healthcare education programs requiring years of study.
Cost breakdowns typically include:
- Tuition and registration fees
- Laboratory supplies and equipment
- Textbooks and educational materials
- Clinical placement coordination fees
- Certification exam fees
- Background check and health clearance costs
Students should request detailed cost information during the application process to understand total financial commitment and plan accordingly.
Program Duration Options
Self-paced online programs allow completion timeframes ranging from 4 weeks to 6 months, providing maximum flexibility for working adults or those with family commitments. Accelerated completion requires significant daily study time, while extended schedules accommodate part-time learning approaches.
Intensive on-campus programs, such as the 9-week format offered by institutions like Mayo Clinic, provide rapid completion with tuition-free options supported by workforce development initiatives. These programs require full-time commitment but offer immediate entry into the workforce upon completion.
Traditional semester-based programs typically require one academic semester for completion, integrating well with college schedules and allowing students to combine phlebotomy training with other coursework or degree programs.
Financial Aid Considerations
Limited financial aid availability characterizes most phlebotomy programs, with many schools not accepting federal financial aid for certificate programs. This limitation requires students to explore alternative funding sources including:
- Employer tuition reimbursement programs
- Workforce development grants
- Private scholarships specific to healthcare training
- Payment plan options offered by training institutions
- Community foundation grants supporting career development
Some students combine phlebotomy training with degree programs that qualify for federal financial aid, spreading costs across multiple semesters while building broader healthcare credentials.
Return on Investment
The relatively low cost and short duration of phlebotomy training create favorable return on investment compared to other healthcare careers. Most graduates recover their educational investment within the first year of employment, making this career path financially viable for many students.
The stable employment prospects and growth potential in healthcare settings provide long-term financial benefits that extend beyond initial salary considerations. Many graduates use phlebotomy experience as a stepping stone to higher-paying healthcare careers, maximizing their educational investment over time.
How to Choose the Right Phlebotomy Certificate Program
Selecting the appropriate phlebotomy technician program requires careful evaluation of multiple factors to ensure the best educational experience and career outcomes. Informed decision-making helps students avoid common pitfalls and maximize their investment in healthcare education.
Accreditation Verification
Verify NAACLS accreditation status before submitting any application materials or financial commitments. Accredited programs meet established educational standards and prepare graduates for national certification exams required by most employers.
Research state licensing requirements for your intended work location, as some states have specific educational requirements that may not be met by all programs. California, Washington, Nevada, and Louisiana maintain state licensing requirements that may specify particular accreditation or curriculum standards.
Contact potential employers in your area to understand their preferred certifications and program requirements. This research ensures your chosen program will meet local employment expectations and provide optimal job prospects upon graduation.
Program Format Evaluation
Consider your learning preferences, schedule constraints, and life circumstances when evaluating program formats. Online programs offer maximum flexibility but require strong self-discipline and independent learning skills.
On-campus programs provide immediate access to instructors and equipment but require regular schedule commitments. Hybrid formats balance flexibility with hands-on instruction but may have limited availability in some areas.
Evaluate the clinical placement assistance provided by each program format. Programs with established clinical partnerships typically provide better externship experiences and employment networking opportunities.
Clinical Placement Assessment
Review the clinical placement assistance and job board access provided to graduates. Programs with strong healthcare partnerships often facilitate better training experiences and employment opportunities.
Investigate the geographic accessibility of clinical sites and whether transportation or housing support is available for required rotations. Clinical placement logistics can significantly impact program completion success and overall educational experience.
Ask about clinical site diversity to ensure exposure to different healthcare environments and patient populations. Varied clinical experience better prepares graduates for diverse employment opportunities and career flexibility.
Success Rate Analysis
Review program statistics including pass rates for certification exams, graduation rates, and employment placement rates. High-performing programs typically maintain detailed outcome data and share this information transparently with prospective students.
Request information about graduate employment rates, starting salary ranges, and employer feedback about program graduates. This data provides insight into program effectiveness and graduate preparedness for professional practice.
Contact recent graduates if possible to gain firsthand insights about program quality, instructor effectiveness, and career preparation adequacy. Graduate testimonials provide valuable perspective on program strengths and potential areas for improvement.
Additional Decision Factors
Evaluate instructor qualifications and experience to ensure access to knowledgeable professionals who can provide current industry insights and practical guidance. Experienced instructors often provide valuable networking opportunities and career mentorship.
Consider program scheduling flexibility and make-up policies for missed classes or clinical sessions. Life circumstances can interfere with educational plans, so understanding program flexibility helps ensure successful completion.
Research continuing education support and alumni resources provided by the institution. Programs that maintain ongoing relationships with graduates often provide career development support and networking opportunities throughout professional careers.
Conclusion
A certificate of phlebotomy represents more than just a credential—it’s your gateway to a stable, rewarding healthcare career that offers both immediate employment opportunities and long-term advancement potential. With 95% of graduates finding employment in their field and growing demand across all healthcare sectors, phlebotomy certification provides a smart investment in your professional future.
The accessibility of phlebotomy training, requiring only a high school diploma and relatively short completion timeframes, makes this career path achievable for diverse backgrounds and circumstances. Whether you choose online, on-campus, or hybrid training, the comprehensive curriculum and hands-on clinical experience prepare you for success in hospitals, laboratories, clinics, and specialized healthcare facilities.
As healthcare continues to evolve and expand, skilled phlebotomy technicians remain essential for accurate diagnostic testing and quality patient care. Your certificate of phlebotomy opens doors to a profession that combines technical expertise with meaningful patient interactions, providing personal satisfaction alongside professional stability.
Take the next step toward your healthcare career by researching accredited programs in your area, understanding the certification requirements, and connecting with admissions representatives who can guide you through the application process. Your journey to becoming a certified phlebotomy technician begins with a single decision to invest in your future—make that decision today.
Application and Financial Aid
Applying to a phlebotomy technician program is a straightforward process, but it’s important to pay close attention to each step to ensure a smooth start to your education. Most programs require prospective students to submit an application form, along with proof of a high school diploma or equivalent. Before submitting your application, review the program’s accreditation information and certification requirements to confirm that the program meets industry standards and will prepare you for national certification exams.
Eligibility requirements may include a minimum age, background checks, and health clearances, so be sure to gather all necessary documentation early. Some schools may also require transcripts, test scores, or letters of recommendation as part of the application process. An application fee is typically required, and tuition costs can vary depending on the institution and the type of phlebotomy technician program you choose.
Financial aid options may be available to help offset the cost of your education. Many programs offer information about scholarships, grants, or payment plans for students who qualify. It’s a good idea to research these opportunities in advance and reach out to the school’s financial aid office for guidance. Remember to factor in the cost of materials, equipment, and any additional fees when planning your budget.
To complete your application, make sure you submit all required documentation by the stated deadlines. Staying organized and proactive during the application process will help you secure your spot in the program and set you on the path to becoming a certified phlebotomy technician.
Phlebotomy Profession and Industry
The phlebotomy profession is an essential part of the healthcare system, with phlebotomy technicians serving as the frontline experts in blood specimen collection and preparation for laboratory testing. As the demand for diagnostic services grows, so does the need for skilled phlebotomists in hospitals, clinical laboratories, outpatient clinics, and physician offices.
Phlebotomy technicians are responsible for drawing blood safely and efficiently, ensuring proper specimen labeling, and maintaining patient comfort throughout the process. Success in this field requires strong communication skills, attention to detail, and the ability to remain calm under pressure. The work of phlebotomists directly impacts the accuracy of laboratory testing and, ultimately, patient care.
The industry is regulated by national accrediting agencies, which set standards for phlebotomy programs and certification exams. Completing an accredited program and passing a recognized certification exam—such as those offered by the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) or the National Healthcareer Association (NHA)—can significantly enhance your career opportunities and earning potential. While some states require national certification for practice, in most other states it is optional but highly recommended to increase hiring potential and salary. Certified phlebotomy technicians are highly valued by employers and often have access to a wider range of positions and advancement pathways within the clinical laboratory and broader healthcare field.
Phlebotomy Resources
Phlebotomy students and professionals have a wealth of resources at their fingertips to support their education and career growth. Accredited phlebotomy programs often provide access to up-to-date textbooks, online learning modules, and hands-on clinical rotations, ensuring students gain both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in clinical laboratory sciences.
Professional organizations such as the National Accrediting Agency for Clinical Laboratory Sciences (NAACLS) offer accreditation information and guidance on program standards. The American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) and the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) are leading providers of certification exams, continuing education courses, and professional development materials. These organizations also host conferences, workshops, and online forums where phlebotomy technicians can network, share best practices, and stay informed about the latest industry trends.
Many schools and training centers offer additional resources, including laboratory testing facilities, study guides, and access to experienced instructors. By taking advantage of these resources, students can enhance their learning, prepare for certification exams, and build a strong foundation for a successful career in phlebotomy.
FAQs and Support
**What are the eligibility requirements for a phlebotomy technician program?**Most programs require a high school diploma or equivalent, and may have additional requirements such as background checks, health screenings, and proof of immunizations.
**How long does it take to complete the program?**Program lengths vary, but many phlebotomy technician programs can be completed in as little as 4 weeks for accelerated online courses, or up to one semester for traditional campus-based programs.
**What certification will I receive after graduation?**Upon successful completion of the program and passing a national certification exam, you will earn a phlebotomy technician certificate, qualifying you for entry-level positions in the field.
**How much does the program cost, and is financial aid available?**Costs vary by institution and program format. Some programs offer financial aid, scholarships, or payment plans. Contact the program director or financial aid office for specific information.
**What job opportunities are available for phlebotomy technicians?**Graduates can find employment in hospitals, clinical laboratories, blood donor centers, and physician offices. Certified phlebotomy technicians enjoy strong job prospects and competitive starting salaries.
**What support services are available to students?**Many institutions provide academic advising, tutoring, career counseling, and job placement assistance to help students successfully complete the program and transition into the workforce. Program directors and admissions representatives are available to answer questions and guide you through the application and certification process.
If you have additional questions or need support, reach out to your program’s admissions office or visit their website for more information. With the right resources and support, you can confidently pursue your goal of becoming a certified phlebotomy technician.

